Introduction to the different types
From the connected factory to virtual assistants, automation has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years. What was once limited to assembly lines now extends to all aspects of the business, revolutionizing the way we work and manage our organizations.
You may be wondering how to navigate this complex automation ecosystem. Indeed, choosing the right solution can seem daunting when faced with the multiplicity of options available. A recent study shows that many companies encounter difficulties when implementing their automation strategy, mainly due to a lack of understanding of the different approaches available.
To help you make the right choices, let's explore the main types of automation, their specific features and their areas of application. From basic IT automation to advanced artificial intelligence solutions, each approach meets specific needs and offers distinct advantages.
Whether you're just starting to think about automation, or looking to optimize your existing processes, this guide will give you the keys to understanding and choosing the solutions best suited to your needs.
2. IT and digital automation (IT and DPA)

Today's digital environment requires companies to make rapid and effective digital transformations. IT and digital automation are often the first step in this evolution, offering affordable solutions for optimizing day-to-day processes.
IT process automation
IT automation is much more than just a series of IT scripts. It encompasses a comprehensive set of practices designed to free IT teams from repetitive tasks, enabling them to concentrate on higher value-added projects.
Key areas include :
- Automatic data backups
- System and software updates
- Network performance monitoring
The strength of this approach lies in its ability to maintain a robust IT infrastructure while significantly reducing the manual workload. For example, a backup that previously took several hours to supervise can now run automatically overnight, with a detailed report sent to the IT team in the morning.
Digital process automation (DPA)
DPA goes further, transforming the way different departments interact digitally. This holistic approach optimizes all digital workflows within the organization.
Practical applications of DPA: Automated invoice management is a perfect illustration of the benefits of DPA. As soon as invoices are received, they are :
- Automatically scanned and filed
- Verified according to predefined rules
- Routed to the appropriate approvers
- Integrated into the accounting system
Strategic advantages
The benefits of automation can be seen on several levels. Beyond the obvious time savings, companies are seeing a significant improvement in their operational efficiency. Teams can now :
- Reduce time spent on repetitive tasks by up to 70%
- Minimize errors related to manual intervention
- Maintain complete traceability of operations
Solutions and implementation
Implementing these automations requires a well-thought-out approach. According to the experts at SnapLogicIt's crucial to start by identifying the most time-consuming, low-value-added processes. Companies can then choose from a range of solutions, from the simplest to the most sophisticated, depending on their specific needs.
3. Robotic process automation (RPA)

Robotic process automation represents a revolution in the way companies manage their day-to-day operations. Contrary to popular belief, these are not physical robots, but intelligent software capable of interacting with applications as an employee would.
Understanding how RPA works
The RPA works like a tireless virtual assistant. According to MicrosoftThis technology excels particularly in automating tasks that usually require repetitive human interaction with different computer applications.
An RPA robot can :
- Connect to multiple systems simultaneously
- Extracting and processing structured data
- Make decisions based on predefined rules
- Generate detailed activity reports
Practical applications by sector
In the financial sector, RPA radically transforms accounting processes. For example, when processing invoices, the robot can automatically extract the relevant information, check it against the purchase order, and initiate the payment process, all in a matter of seconds.
For human resources, the impact is just as significant:
- Automatic creation of access for new employees
- Synchronized updating of various HR databases
- Automatic generation and dispatch of administrative documents
Concrete benefits and ROI
Implementing RPA generates quantifiable benefits:
Operational precision improves considerably, with a near-zero error rate for well-configured tasks. Productivity gains are also remarkable: an RPA robot can work 24/7 without interruption, multiplying administrative task processing capacity.
Financial considerations :
- Return on investment generally seen in 6-12 months
- Significant reduction in operating costs
- Savings on overtime
Key success factors
The success of an RPA project depends on several critical elements. It is essential to :
Start with a thorough analysis of existing processes. Not all processes lend themselves to RPA automation, and it's crucial to identify those that will offer the best return on investment.
Pay particular attention to :
- Training the teams supervising the robots
- Detailed documentation of automated processes
- Setting up a quality control system
4. Industrial automation and robotics
Industrial automation is the historical foundation of manufacturing modernization. Today, it is undergoing a new revolution with the integration of intelligent technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT), transforming traditional factories into truly connected production sites.
The four pillars of industrial automation
1. Fixed automation represents the most traditional form of industrial automation. Particularly suited to mass production, it features a unique configuration optimized for a specific type of product. Although not very flexible, it offers maximum efficiency for large production runs.
2. Programmable automation adds a new dimension by enabling equipment to be adapted to different production runs. A typical example is CNC machine tools, capable of producing different parts according to the programs loaded.
The other two types represent the modern evolution of automation:
3. Flexible automation combines agility and efficiency. It enables :
- Switch quickly between different productions
- Maintaining high productivity
- Adapting to variations in demand
- Optimizing the use of resources
4. Intelligent automationthe most recent, integrates artificial intelligence to create systems capable of autonomous learning and adaptation. This revolutionary approach enables continuous optimization of production processes.
Concrete applications in industry
The impact of these technologies can be seen in various aspects of production. In a modern assembly line, we can observe :
Intelligent coordination between robots and human operators, where each focuses on its strengths. Robots handle repetitive or dangerous tasks, while humans supervise and intervene in aspects requiring judgment and adaptation.
Automated quality control systems use :
- High-definition cameras
- Sophisticated sensors
- Real-time analysis algorithms
- Integrated traceability systems
Strategic and operational benefits
Modern industrial automation brings substantial benefits:
Productivity increases significantly thanks to :
- Constant speed of execution
- Reduced downtime
- Continuous process optimization
Quality is improved by :
- Perfectly repeatable operations
- Systematic quality control
- Complete traceability
Implementation considerations
Implementing effective industrial automation requires a methodical approach. In particular, companies must :
Accurately assess their current and future needs in order to choose the most appropriate type of automation. This analysis must take into account not only the technical aspects, but also the human and organizational implications.
Particular attention should be paid to :
- Ongoing staff training
- Scalability of chosen solutions
- Preventive maintenance
- Integration with existing systems
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning

The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in automation represents a major qualitative leap forward. These technologies transform previously rigid systems into adaptive solutions capable of learning and evolving according to the situations encountered.
A new dimension in automation
AI and ML bring a capacity for analysis and adaptation that traditional automation could not offer. Instead of simply following predefined rules, these systems can :
Analyze complex situations and make nuanced decisions based on :
- Data history
- Current trends
- Forecasts generated
- Anomalies detected
Concrete applications in various sectors
In e-commerce, AI is revolutionizing the customer experience through :
Advanced offer personalization. The system analyzes user behavior in real time to make relevant recommendations, significantly boosting conversion rates.
For the financial sector, applications include :
- Real-time fraud detection
- Automated risk assessment
- Optimizing investment portfolios
- Intelligent automated customer service
Intelligent automation in production
In the industrial environment, AI is transforming predictive maintenance. Systems can now :
Anticipate breakdowns before they happen by continuously analyzing :
- Machine vibrations
- Operating temperatures
- Electricity consumption
- Abnormal sound patterns
This proactive approach significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Distinctive advantages
Integrating AI into automation brings unique benefits:
Unprecedented adaptability: Systems automatically adjust to changing conditions, continuously optimizing performance without human intervention.
Improved decision-making thanks to :
- Real-time analysis of massive data
- Recognition of complex patterns
- Continuous learning from past experience
Challenges and considerations
Implementing these advanced technologies requires in-depth consideration of :
Data quality: The effectiveness of AI systems depends directly on the quality and quantity of the data available. A robust data collection and management strategy is crucial.
Practical aspects include:
- Training teams in new technologies
- Managing organizational change
- Data security and confidentiality
- Scalable solutions
6. Business process automation (BPA)

Business Process Automation (BPA) represents a holistic approach to automation, aimed at optimizing all of a company's operational processes. Unlike fragmented approaches, BPA offers a unified vision of automation, aligned with the organization's strategic objectives.
A holistic approach to automation
BPA is distinguished by its ability to :
Orchestrate complex processes involving multiple departments and systems. For example, an invoice approval process can automatically cross purchasing, accounting and management departments, while respecting the validation rules specific to each level.
Typical business processes include :
- Customer order management
- Approval workflows
- Report generation and distribution
- Inter-departmental coordination
Integration and coordination
The effectiveness of the BPA lies in its ability to integrate. A concrete example: when onboarding a new employee, the :
Automatically coordinates all necessary actions:
- Creating computer access
- Workstation configuration
- Planning initial training courses
- Preparation of administrative documents
This orchestration guarantees a smooth, standardized experience, significantly reducing delays and errors.
Technologies and tools
BPA is based on a number of complementary technologies:
Specialized platforms allow you to :
- Graphical process modeling
- Define business rules
- Monitor performance
- Adjust workflows in real time
Organizational benefits
The impact of GAP can be measured on several levels:
Operational efficiency : A recent study shows that companies using BPA find :
- 30% reduction in processing times
- A 25% reduction in operating costs
- 40% improvement in customer satisfaction
Qualitative advantages :
- Process standardization
- Better regulatory compliance
- Enhanced traceability
- Reducing team stress
Key success factors
The success of a BPA project requires careful attention to several aspects:
Prior analysis of existing processes is crucial. You need to :
- Identify bottlenecks
- Understanding interactions between services
- Define clear performance indicators
- Involving end users
Implementation should be gradual, starting with the most critical processes or those offering the most significant quick wins.
Future prospects
BPA continues to evolve with the integration of new technologies:
- Artificial intelligence for continuous optimization
- Predictive analysis to anticipate needs
- Conversational interfaces to simplify interactions
- Cognitive automation for complex decisions
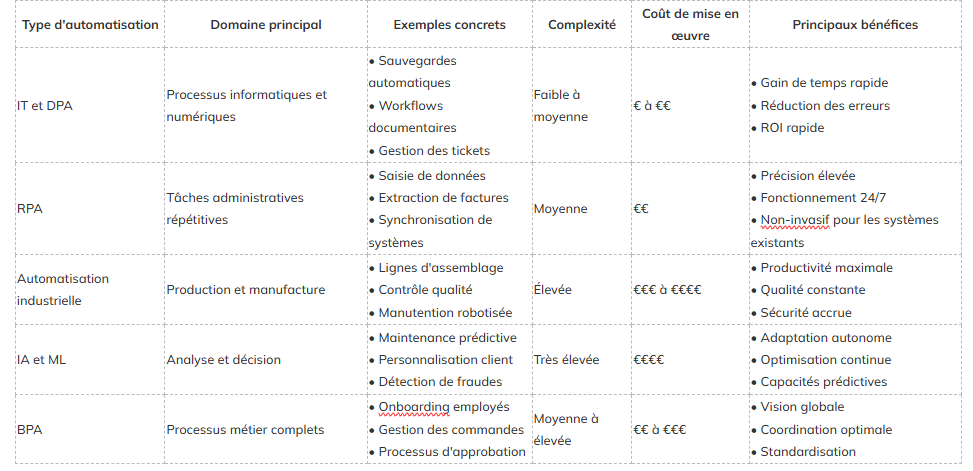
7. Comparison of automation types
To facilitate understanding and decision-making, here is a detailed comparative analysis of the different types of automation:
8. Conclusion
Today, automation is much more than just a technological option: it has become a strategic imperative for companies wishing to remain competitive in an ever-changing economic environment.
Summary of key points
The diversity of automation solutions enables us to meet a wide range of needs:
From the simplest to the most complex :
- IT automation for everyday tasks
- RPA for repetitive processes
- BPA for a global approach
- AI/ML for the most complex challenges
Practical recommendations
For successful implementation, we recommend :
- Start with a thorough audit of existing processes
- Identify "quick wins" to quickly demonstrate value
- Adopt a progressive, methodical approach
- Train and support teams throughout the process
Automation is not a destination, but a continuous journey towards operational excellence. Success lies in the ability to choose the right solutions and implement them thoughtfully and progressively.
9. FAQ - Frequently asked questions about automation solutions
1. What types of automation are there?
The main types include :
- Digital Process Automation (DPA): simplifies digital workflows.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): imitates human actions on systems.
- Business Process Automation (BPA): optimizes overall business processes.
- Industrial automation: fixed, programmable, flexible and intelligent.
2. What's the difference between EPS and GAP?
- RPA automates specific tasks such as data entry.
- BPA aims to optimize complete business processes.
- Example: RPA fills out an invoice automatically, while BPA manages the entire invoice processing workflow.
3. What are the advantages of different types of automation?
- DPA Simplifies digital workflows.
- RPP Reduces human error and speeds up repetitive tasks.
- BPA : Optimizes inter-departmental collaboration.
- Industrial automation Increases productivity and guarantees consistent quality.
4. How to choose the right type of automation for your business?
Analyze your needs:
- For simple repetitive tasks: RPA.
- To optimize complex flows: BPA.
- For industrial production: choose between fixed, flexible or intelligent automation, depending on your objectives.